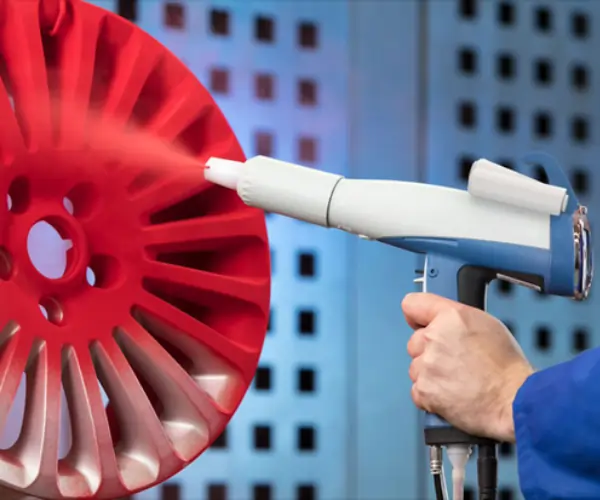
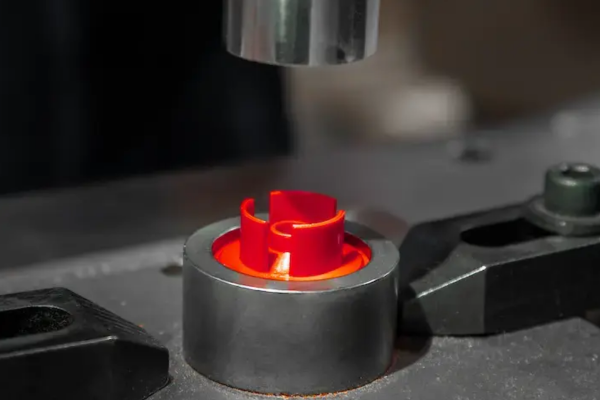
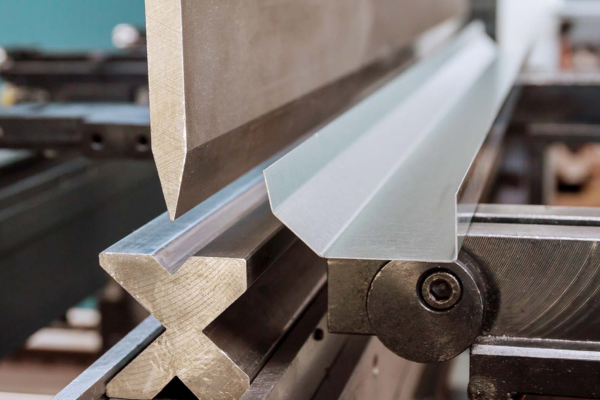
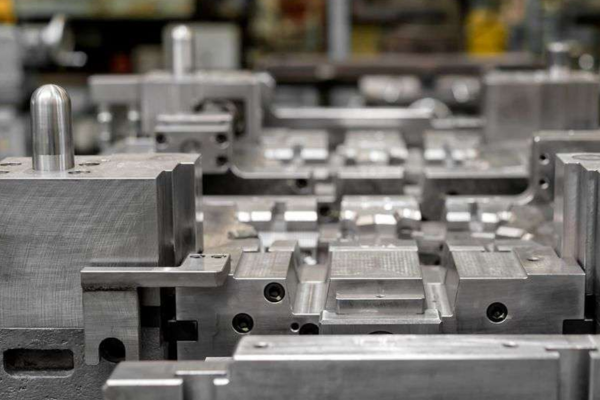
In the world of additive manufacturing, where innovation and precision are paramount, Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) technology stands out as one of the most promising advancements in 3D printing. At XC Machining, we harness the power of MJF to create high-quality, complex parts with unmatched precision, speed, and efficiency.
¿Qué es la fusión multichorro (MJF)?
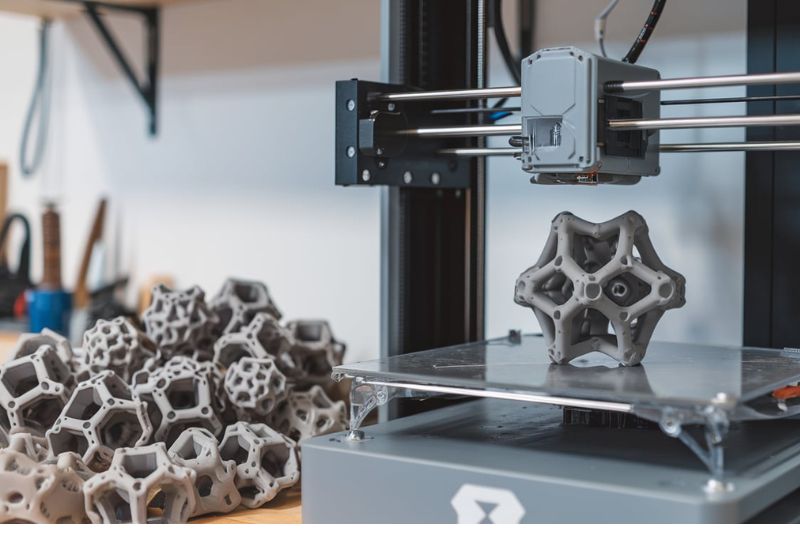
Multi Jet Fusion is an advanced 3D printing technology that uses a powder bed fusion process. It was developed by HP (Hewlett-Packard) and has since become a preferred choice for producing end-use parts, functional prototypes, and highly detailed components across various industries. MJF uses a fine powder material that is selectively fused using a combination of inkjet printing and heat to create detailed parts layer by layer.
Unlike traditional 3D printing methods, MJF utilizes an array of printheads that deposit binding agents onto the powder bed. These agents are followed by infrared light, which activates the fusion process. The result is a dense, high-quality, fully functional part without the need for additional supports, reducing waste and improving overall efficiency.
The MJF Process at XC Machining
At XC Machining, we utilize state-of-the-art MJF printers to produce high-precision, durable parts with remarkable speed. Our MJF process follows several key steps to ensure the highest quality output:
Preparation and Setup
The process begins by preparing a 3D model of the part, which is typically designed using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. Afterward, the model is sliced into thin layers, which are sent to the MJF printer. This digital model guides the deposition of the binding agents and fusion steps during the printing process.
Powder Bed
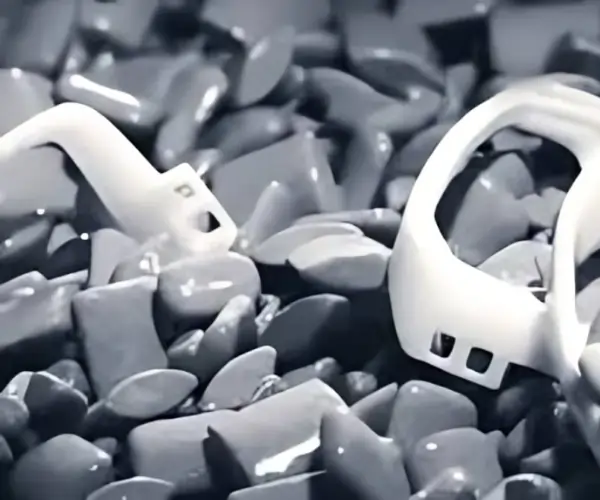
A thin layer of fine powder, often nylon-based, is spread across the build platform of the MJF printer. The powder acts as both a medium for printing and a support structure, enabling the construction of intricate geometries without the need for additional support structures.
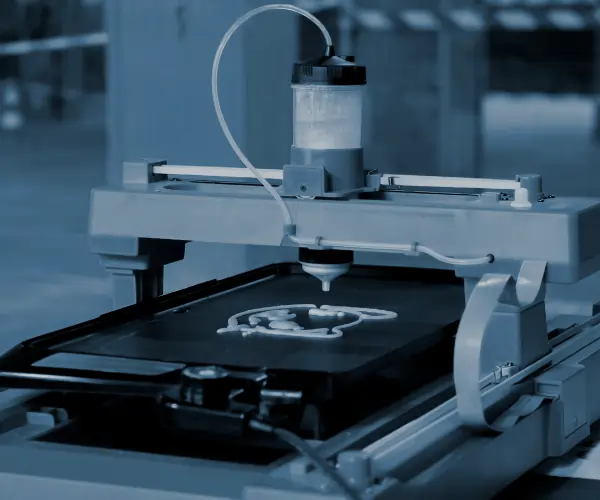
Binding Agent Deposition
The printhead moves across the powder bed, spraying a liquid binding agent onto the powder. This agent acts as the “glue” that holds the powder particles together and forms the basis of the part. The printhead also sprays different materials to give the part different properties, such as enhanced flexibility, strength, or conductivity.
Infrared Heating
After the binding agent is deposited, the printer’s infrared light system selectively heats the powder. This step fuses the powder particles together, creating solid layers that gradually build up into the final part.
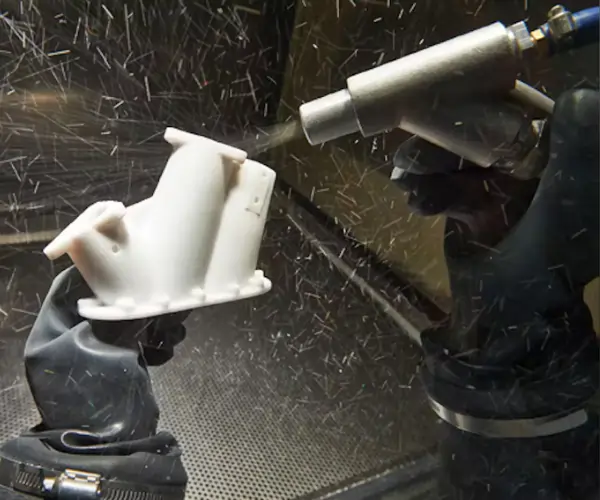
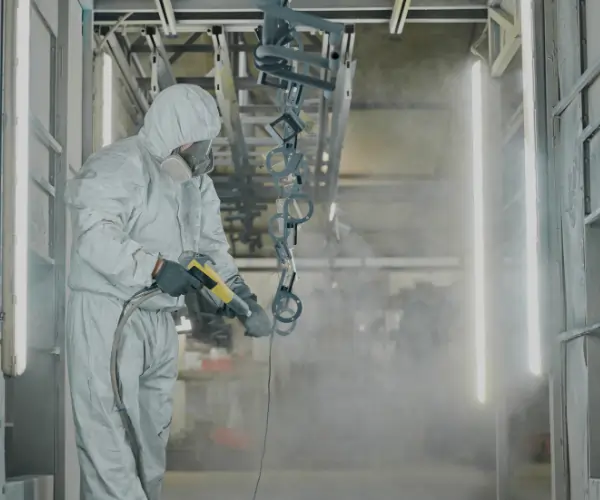
Cooling and Post-Processing
After each layer is fused, the printer’s build platform is lowered, and another layer of powder is spread. This process is repeated until the part is complete. Once the printing is finished, the part is allowed to cool down before being carefully removed from the powder bed.
Advantages of Multi Jet Fusion at XC Machining
High Precision and Complex Geometries
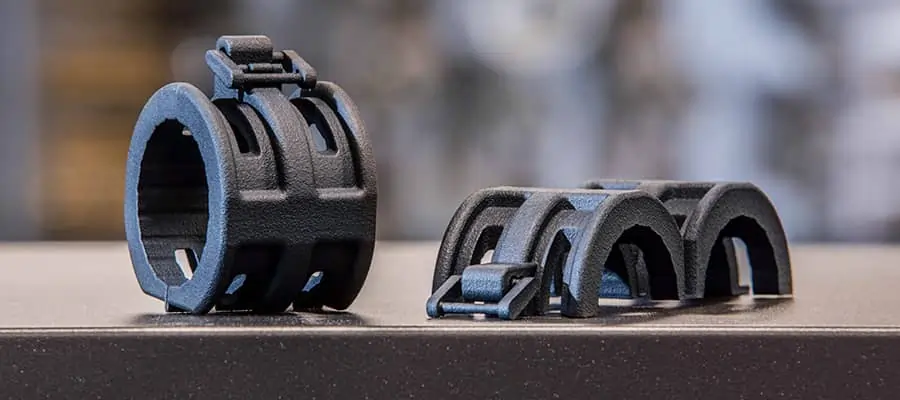
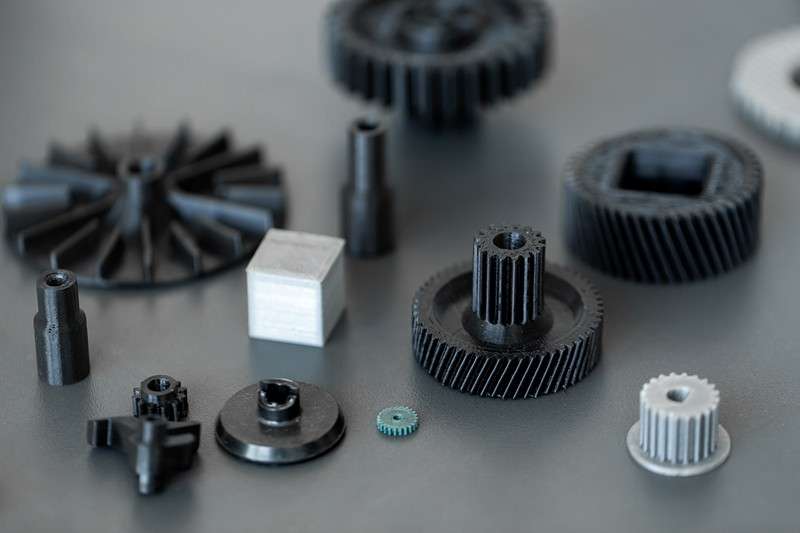
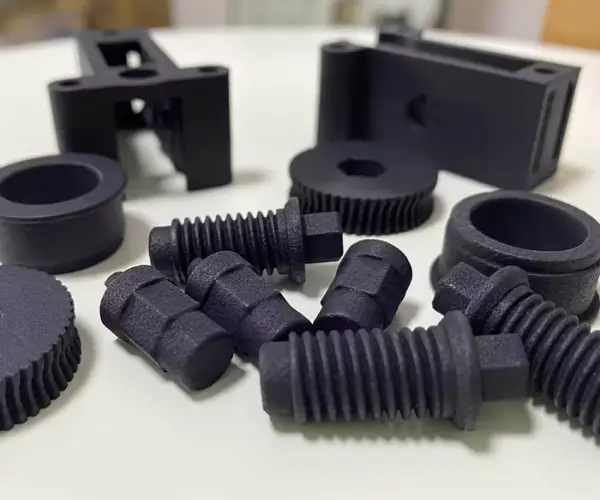
One of the major advantages of MJF over traditional manufacturing methods is its ability to create highly detailed and intricate parts. The printing process is incredibly precise, allowing us to produce components with complex geometries, fine details, and tight tolerances. This makes MJF an excellent choice for industries that require complex and customized parts, such as aerospace, medical devices, and automotive.
Velocidad y eficacia
MJF technology is incredibly fast compared to other 3D printing methods like SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) or SLA (Stereolithography). The process is highly parallel, meaning multiple parts can be printed simultaneously within a single print cycle. At XC Machining, this speed reduces turnaround times and ensures faster delivery of products to our clients.
Eficiencia material
MJF operates with minimal material waste. Unlike other technologies that require support structures or excessive post-processing to remove excess material, MJF uses a powder-based system where unused powder can be recycled and reused. This not only minimizes waste but also makes it an environmentally friendly choice for manufacturers.
Personalización y flexibilidad
MJF offers exceptional flexibility in terms of part customization. Designers can adjust the part’s properties during the printing process, such as varying the part’s density or surface finish. This capability allows for the production of bespoke parts with specific mechanical properties that meet the unique needs of each client.
Cost-Effective for Low-Volume Production
MJF is an excellent choice for low-volume production runs due to its quick setup time and minimal tooling requirements. Since the process does not require expensive molds or dies, MJF offers a cost-effective solution for manufacturing prototypes and small to medium-sized production runs.
Our team of engineers and technicians are experts in the MJF process, ensuring that each part is printed to the highest standards of quality. Whether you’re looking for prototypes, end-use parts, or custom components, XC Machining has the expertise and capabilities to deliver.
We understand that each project is unique, and we work closely with our clients to ensure their specific needs are met. Our dedication to customer satisfaction, along with our advanced MJF technology, makes us a trusted partner for businesses looking to innovate and streamline their manufacturing processes.