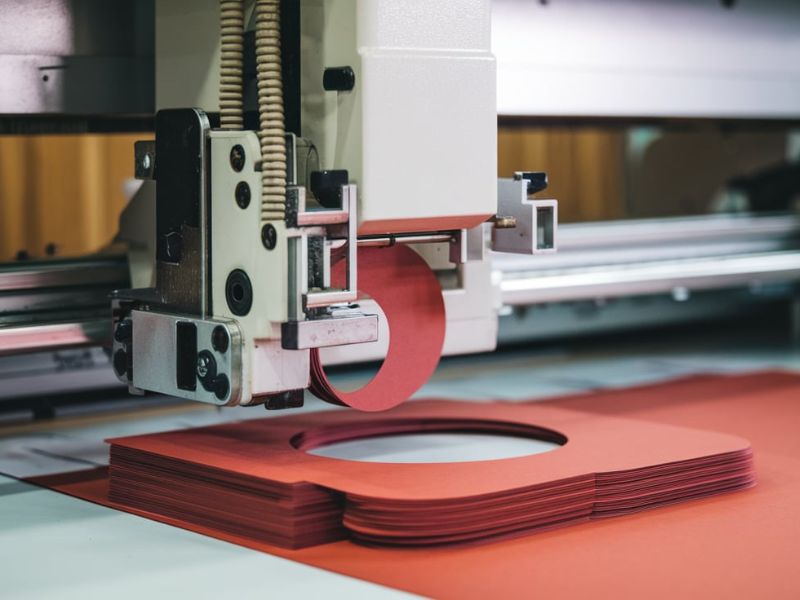
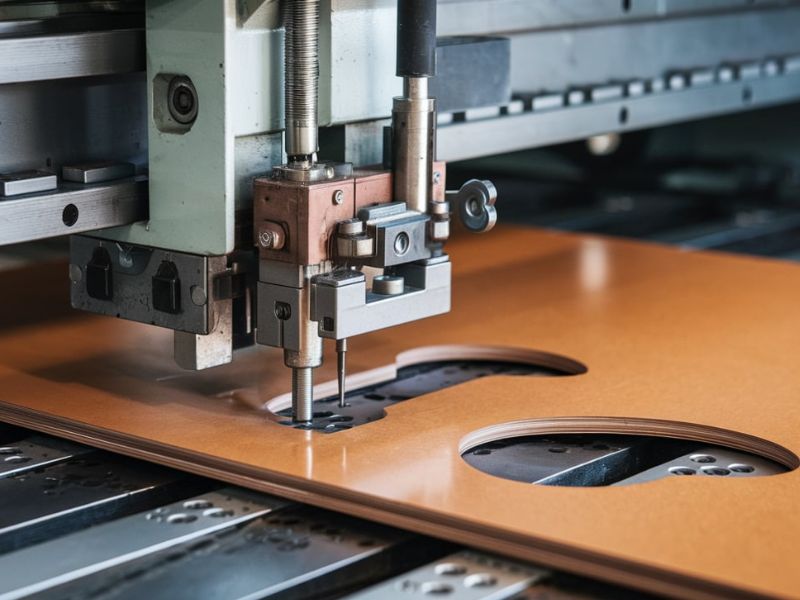
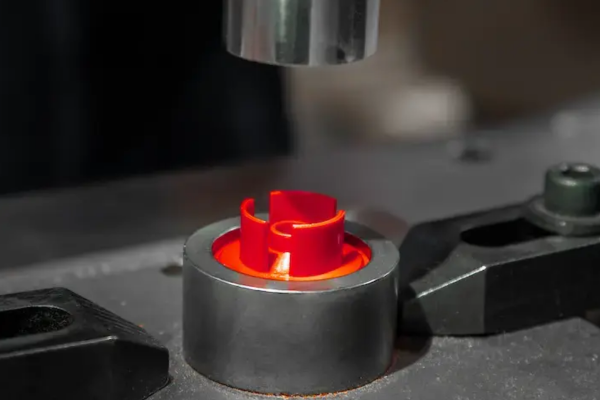
Die cutting is the manufacturing process used in cutting of materials into specified shapes or designs. It’s a process in which a material like paper, fabric, plastic or rubber is shaped to be cut or cut into a specific shape using a die (a special tool or mold). Here’s how the process typically works:
Design and Die Creation
It starts with the planning of what shape or pattern one wants through the program-CAD (Computer-Aided Design). When the design is complete, it is fabricated using die, that is, a specially made tool that matches the exact pattern or shape. The die is either made of steel or other long-lasting material depending on the complexity and the amount of the project to be done.
Selection and Preparation of Materials
The next process is choosing the material that would be cut. There is a huge diversity of materials: it can range between paper and cardboard, plastic, and metal. After the selection of the material, it is prepared and placed on a die-cutting machine. The material should be cut after properly aligning because this will determine where the cuts should be made.
Die Cutting
The real cutting process on the die takes place when the die is forced on the material under great pressure. These sharp edges are used to cut through the material to shape it to the desired effect. Depending on the material and complexity of the design, it may use rotary die cutting (using a rotary die) or flatbed die cutting (using a flat die).
Finishing and Quality Control
Once the material is cut it can go on further stages like trimming, embossing and even making them perforated. The quality, thereafter, is checked on the cut parts and the required specifications are met. This is an essential step to eliminate the shortcomings or fluctuations of the cuts.
Packaging and Delivery
After approval processes of the custom die cuts, the pack is finally delivered to the customer. It can be highly customized in terms of its use: depending on the need, the end product may be used as packaging, labels, gaskets or any other application.
Challenges in Custom Die Cutting and How They Are Solved?
The die cutting process raises a lot of considerations, and it is essential to ensure that everything concerning design, materials, and manufacturing methods are put in check to meet the best outcomes.
Material Defects
A challenge of custom die cutting is the possibility of defects in the materials of use uneven thickness, creases or tears. The precision and uniformity of the cuts can be subject to these problems.
Solution: Metal suppliers thoroughly choose and test the materials before another process of cutting can begin. A high grade of materials is used which is uniform in thickness, and the die cutting machine is adjusted to have satisfactory cutting pressure. Periodic upkeep of the machine also avoids the defects.
Coûts d'outillage
The cutting needs high precision tooling, something which can be very expensive to design especially in case of low quantities or special orders. The fact that there is high upfront cost involved in manufacturing custom dies may ensure limited runs are not quite cost effective.
Solution: Manufacturers are able to optimize die designs to eliminate unnecessary complexity, and to increase life. Rotary die cutting can be an option on smaller runs, as some firms offer up such cylindrical dies that can be cheaper. CAD and simulation software are also used to produce efficient die designs so as to minimize the occurrence of frequent re-tooling.
Accuracy and Tolerances Dimensional
When very strict dimensional accuracy is required, it is necessary. Miscuts can occur due to variations in material thickness or die alignment and this might render the end product unusable.
Solution: In order to enhance dimension accuracy, the manufacturers equip their high precision die-cutting machines with automated controls. The machines are also frequently serviced to achieve accuracy. Appropriate alignment of the material and die is also done to ensure that the cuts are uniform and of the desired tolerances.
Déchets matériels
The die cutting method has sometimes an excessive waste with some types of materials, especially when the material is not in the optimum placement position on the die.
Solution: Manufacturers also plan the arrangement of cuts so as to maximize the space possible in the material to reduce wastage. Nesting programs aid in layout of the cut patterns to minimize waste, and also increase the use of incoming materials. Also, waste recycling systems can be installed in order to reuse any excess material.
Fastness and Swiftness
Cutting may at times be a time consuming method specially where the design is not simple or when using the materials that are thick. High-volume production always requires a high speed to operate and any delay in the process will increase the lead time.
Solution: Rotary die cutting can be used by manufacturers to speed up cycle times since there is continuous feed of the material and increased production rates. On thicker materials, special cutting dies are applied that ensure high-speed results without the loss of precision.
Environmental and Safety concern
In Die cutting, there is the use of materials and machine tools that may be harmful to the environment and employees, in particular, when dealing with some of the chemical components or sharp sides.
Solution: Many manufacturers are moving to eco-friendly materials, e.g. recycled paper or bio-degradable plastics to have less environmental impact. With regard to safety, there are machine safety features like automatic shutoffs, safeguarding covers, and sensors that are installed. Protective equipment is also offered to workers in order to protect their safety at the workplace.