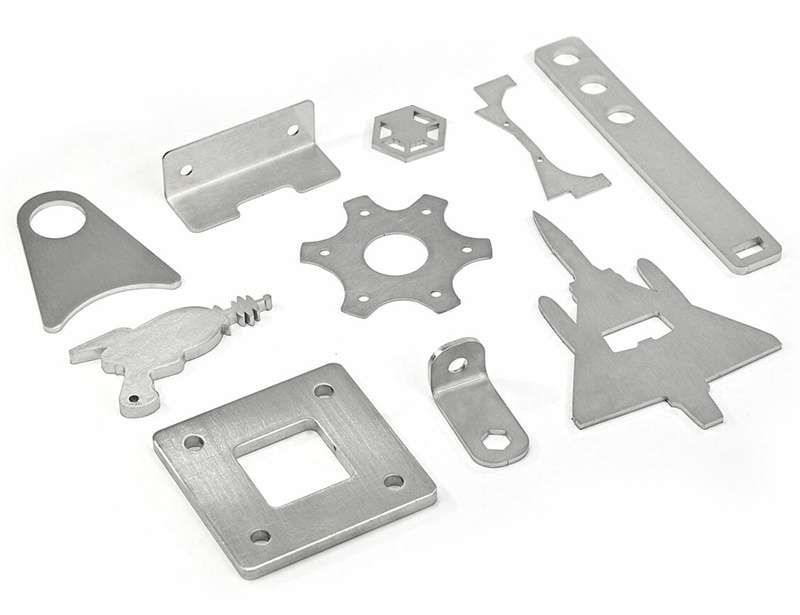
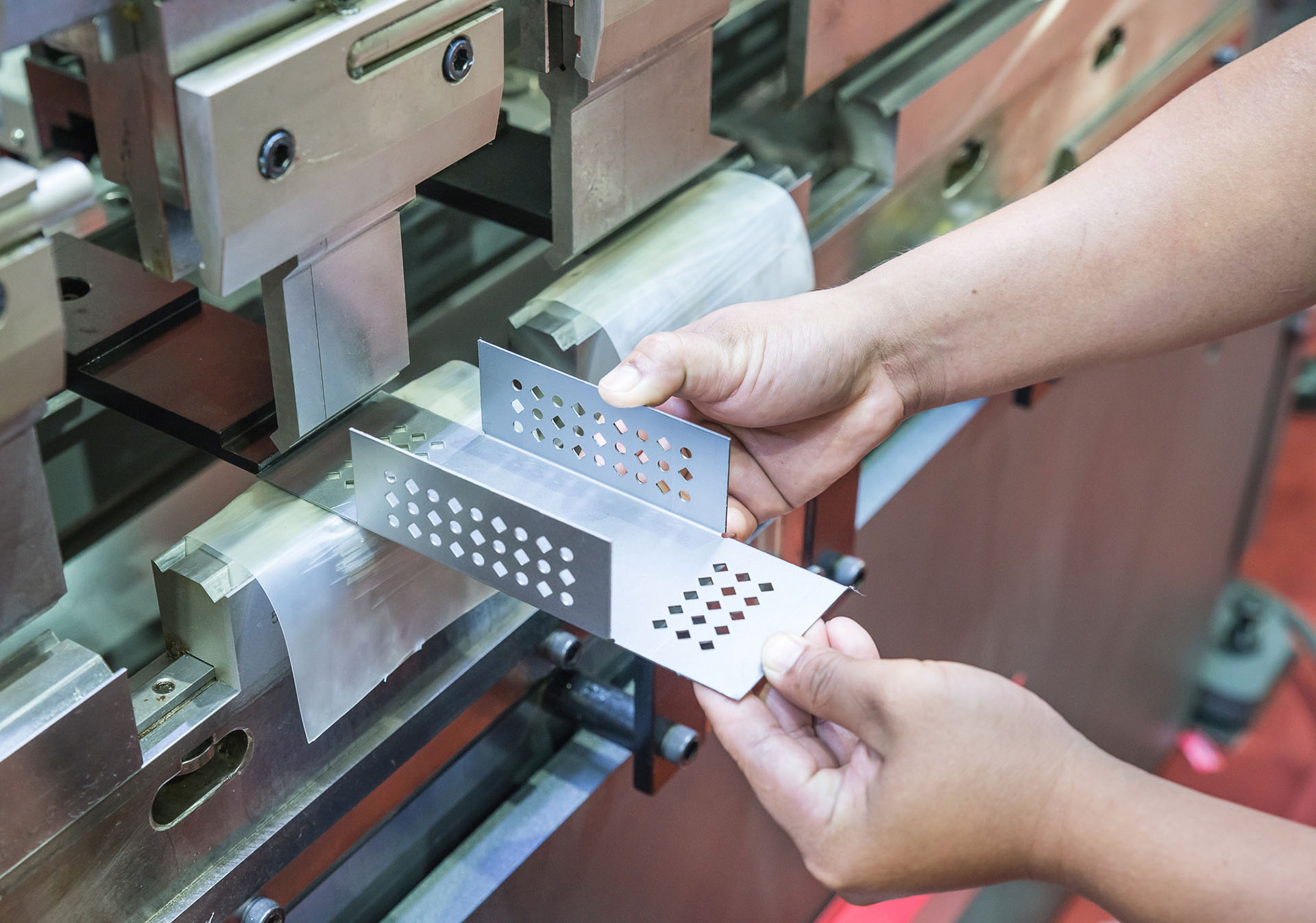
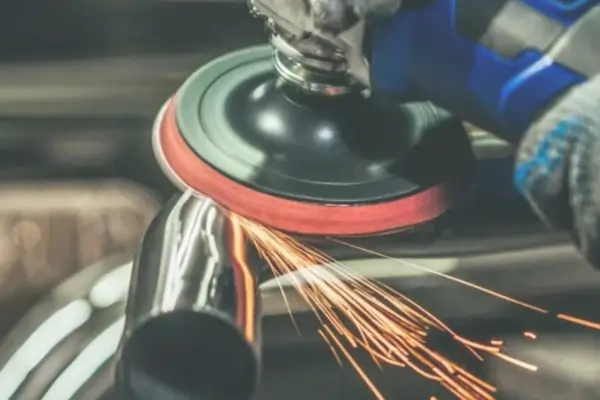
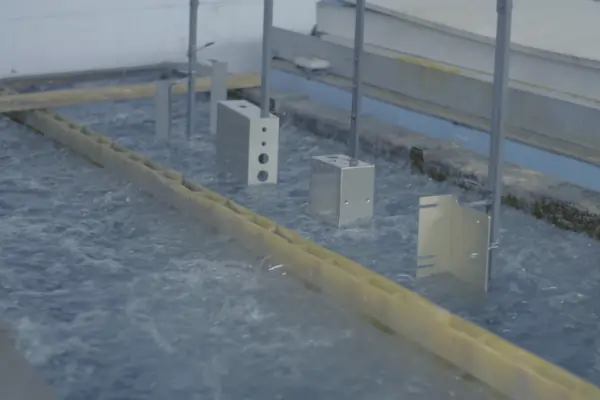
Sheet metal fabrication is a manufacturing process which changes metal sheets in order to form functioning structures or parts using the process of cutting, forming, joining and finishing. It integrates engineering with advanced machinery to produce custom parts in industries.
Here’s a step by step guide of the way the mechanism works:
1. Design & Engineering
Every project starts with a technical drawing file or 3D CAD file. The design is checked by engineers and its tolerance is figured out and appropriate materials used (such as stainless steel, aluminum or galvanized steel) depend on the strength of the application, its resistance to corrosion and the weight requirement. This is important since the Early design review assists in finding cost saving possibilities and maximization of manufacturability.
2. Materials Selection and Preparation
The appropriate metal sheets are selected in terms of thickness (gauge), finish and the grade of material. After this, these sheets are washed, and ready to be processed to make sure there is accuracy and quality in fabrication. Materials used to make the sheet metal can include, Aluminum, stainless steel, mild steel, copper, brass.
3. Cutting
The metal sheet is then cut into the necessary form and dimension depending on the design file using CNC laser cutting, plasma cutting or waterjet cutting. Laser cutting provides a very tight tolerance and clean edges of complex parts.
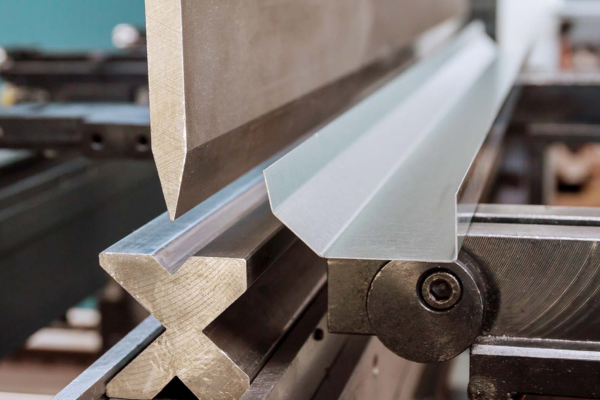
4. Forming & Bending
The flat sheet is then shaped into 3D forms using techniques like:
- Press braking for bending angles.
- Stamping for high-volume part formation.
- Rolling for cylindrical shapes.
This stage creates the physical geometry of your final part like enclosures, brackets, or panels.
5. Joining & Assembly
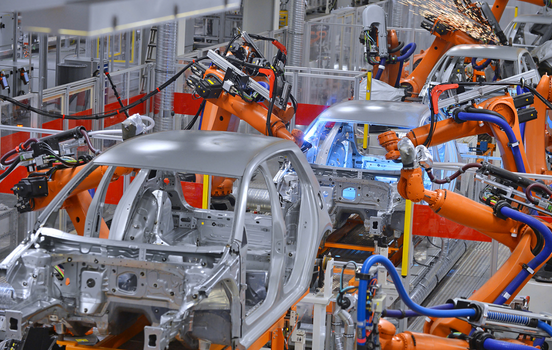
At this stage, weld (TIG, MIG or even spot welding) is done to join the metal parts together on a permanent basis so as to be strong and durable.
- Welding (TIG, MIG, or spot welding) is used to fuse metal parts permanently, ensuring strength and durability.
- Riveting involves inserting metal pins to securely join overlapping sheet metal components.
- Fastening uses screws, bolts, or other mechanical hardware for detachable and serviceable joints.
- Adhesive bonding applies industrial-grade adhesives to create smooth, clean joints without heat or mechanical stress.
6. Finishing
- Deburring is done in order to remove sharp edges and burrs left after the operation, to result in smooth surfaces and safe handling.
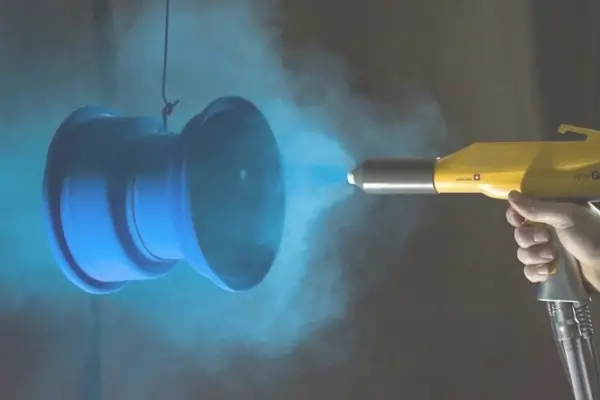
- Powder coating is the process that is carried out by applying a dry powder electrostatically and curing it to produce a superior and appealing finish that is durable.
- Anodizing enhances the natural oxide layer on aluminum, increasing corrosion resistance and wear protection.
- Painting provides a protective and decorative coating by use of painting which is also in numerous colors and finishes.
- Galvanizing plays the role of providing a deposit of zinc on the metal to prevent rusting and other effects associated with the environment.
Such finishing also makes the product more resistant to corrosion, looks better, and has a longer period of life.
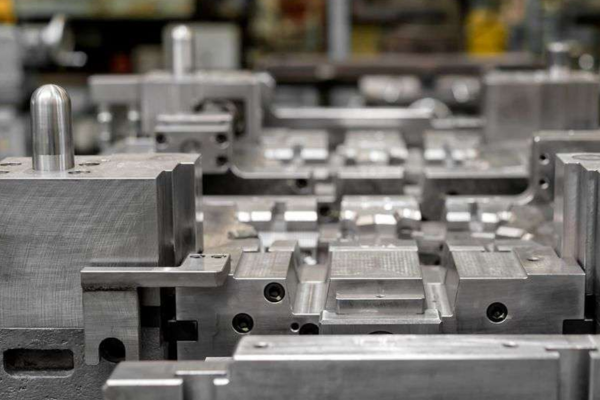
7. Inspection & Quality Control
Every part or assembly is thoroughly checked with the help of calipers, gauges, CMM machines or laser scanners in order to guarantee that it adheres to requirements on the dimensions, strength and surface condition. Such a precaution guarantees a lot of precision and dependability prior to delivery.
8. Packaging & Delivery
When it has been passed, the final products are then finally packaged well to avoid any form of damage to them and then either shipped to the destination of the client or incorporated to make a bigger component in a line of products. Protective materials, labelling, and organisation of logistics help us to make sure that our every order is delivered without delay, in a safe and traceable way.
How Precise Is the Sheet Metal Fabrication Process?
Sheet metal fabrication offers excellent precision, especially when the entire process is controlled using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology. The accuracy is determined by the technique, material and product tolerance with industrial standards up to ultra-fine precision coolant-cutting work where required by aerospace and high precision medical components.
Key Factors Affecting Precision in Sheet Metal Fabrication
A variety of things can interfere with the accuracy of finished part:
- Type and Thickness of Material: A sheet of a material is more likely to get distorted when the material is thin (i.e., aluminum).
- Cutting Method: The laser cutting (CNC) is more precise than plasma or waterjet.
- Quality of equipment: The labor force uses good quality equipment such as robotic press breaks and advanced fiber lasers that provide tighter tolerances.
- Skill and Set Up: Skilled technicians, proper fixturing, and precise calibration reduce human error.
- Design and Engineering: CAD files should be produced with clear specification of tolerances to make high quality production very efficient.
Ready to Start Your Sheet Metal Project?
Precision, speed and engineering experience are just some of the things that make XC Machining your choice for high quality sheet metal parts the way you want them in the sizes needed. Our team will help you regardless of whether you require prototypes, low-volume productions or large scale productions.
Contact us today to get a custom quote to upload a CAD file or some other consultation with our professionals according to your fabrication needs.